11:00am to 2:30pm IST
( Both Online and Offline batches)
MEP stands for Mechanical Electrical and Plumbing. It’s a branch of engineering that deals with designing and implementing heating and ventilation circuits, electrical systems and plumbing of buildings.
MEP systems were designed together to avoid conflicts between the 3 of them. The possibility of interaction between them is very high in any type of building that uses these 3 systems. the complication in the MEP designs will vary in the types of buildings like houses, shopping malls, hospitals, hotels etc..
Now days the contracting company as well as client wants more MEP person. In India and Middle East Less MEP contracting company is working like, Voltas, Tata projects, Blue star, sterling & Wilson, shapoorji & pallonji etc but in consultancy & client side there are huge vacancy in MEP sector because due to the basic which was not clear from theory. The person need to more practical knowledge rather than theoretical knowledge. So if you wants to be MEP engineer you should have theory & practical depth knowledge.
Typically, entry into the MEP engineering world is through an education in electrical, mechanical or related engineering field. A bachelor’s degree will open the door towards becoming an Engineer-in-Training, which then leads to the potential of becoming a Licensed Professional Engineer. An associate’s level education, typically in CAD or REVIT, leads towards becoming an MEP designer.

The mechanical aspect deals with heating ventilation and air conditioning systems. The function of this is to make the building at optimum temperature. Which will help to live inside is more comfortable.
In general, the mechanical section is dealing with:
-Heating
-Ventilation and
-Air conditioning.

The electrical section ensures the proper functioning of the electrical systems of the building. The proper electrical system is as cost-effective and simple as possible. The MEP Engineer works to make the electrical circuits and systems as soon as possible.
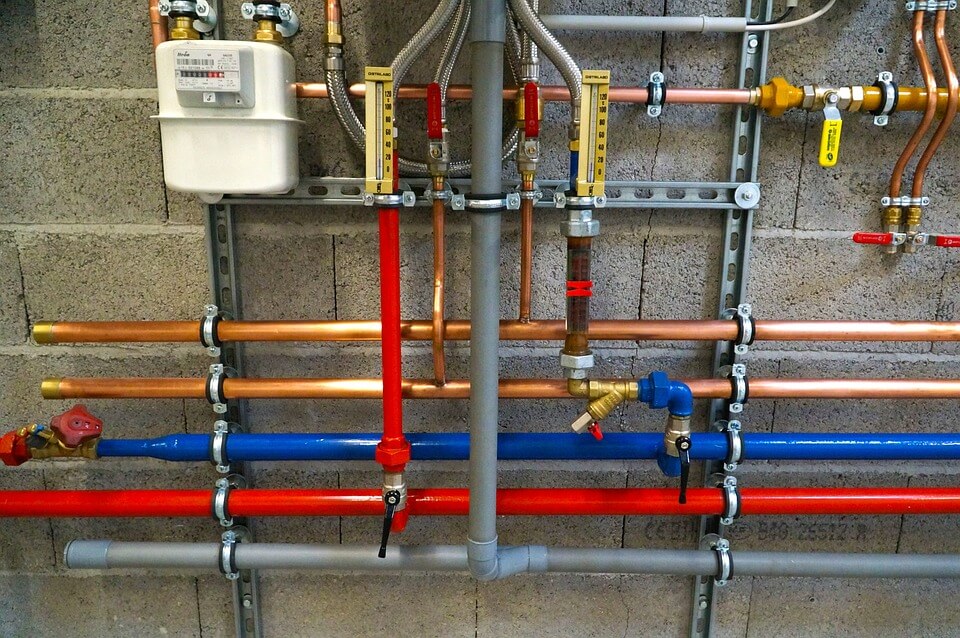

It is to ensure water flow. The plumbing section as it names itself says all. In this section, the system is for ensuring the plumbing circuits works well without any complication. The plumbing circuits include water supply, wastewater disposal, acid waste systems…etc. According to the purpose of the building. A normal House apartment will have water supply and wastewater (other human waste) disposal sections. It will be very sophisticated when it comes to a factory, hospitals, plants…etc.








This course is intended to introduce users to the software’s user interface and the basic HVAC, electrical, and piping/plumbing components that make the Autodesk Revit software a powerful and flexible engineering modeling tool. The course will also familiarize users with the design concepts of MEP engineering. The examples and practices are designed to take the users through the basics of a full MEP project from linking in an architectural model to construction documents.
⮚Fundamental and scope of HVAC
⮚Mode of heat transfer
⮚Standards
⮚Refrigeration cycle
⮚Component of A/C
⮚Refrigerants and types
⮚Window Air Conditioning Systems.
⮚Split Air Conditioning Systems
⮚Central Air Conditioning Systems.
⮚Package Air Conditioning Systems.
⮚Properties of Air (DBT, %RH, WB, DPT, enthalpy).
⮚Load Calculation.
⮚Orientation of Building
⮚To Read Latitude of Location of building
⮚Calculation of U factor for wall, glass, Roof and Partition .
⮚Calculation of Equivalent Temp.
⮚Difference for wall, glass, Roof and Partition
⮚Cooling and Heat Load Calculation
⮚ASHRAE Standards
⮚Calculation Of sensible Heat Factor, ADP and Dehumidified CFM
⮚Study about Chilled Water Systems
⮚Types & Application of Chillers
⮚Open loop & Closed loop system- Chilled water pipe sizing
⮚Types of Valves & Its Connection
⮚Primary and Secondary pump system,
⮚Components of Chilled Water system
⮚Calculation of duct sizes by Mc-Quay Duct Sizer
⮚Air terminal selection.
⮚Selection of Materials of Ducts.
⮚Primary and secondary pump selections.
⮚Selection of cooling tower.
⮚Selection of Chillers.
⮚AHU and FCU classification and selection.
⮚Package unit selection DX unit selection
⮚Chilled water pipe sizing.
⮚Calculation of Chilled water pipe sizes by Mc-Quay pipe Sizer Software.
⮚Ventilation, Infiltration load calculations.
⮚Restaurant and residence kitchen ventilation system design.
⮚Parking area ventilation and designing.
⮚Toilet ventilation (Industrial and residential).
⮚Hourly analysis program (HAP)
⮚Psychrometric calculator
⮚Mc-Quay Duct Sizer
⮚ BIM and Autodesk Revit
⮚ Overview of the Interface
⮚ Starting Projects
⮚ Viewing Commands
⮚ Using General Sketching Tools
⮚ Inserting Components
⮚ Selecting and Editing Elements
⮚ Working with Basic Modify Tools
⮚ Working with Additional Modify Tools
⮚ Linking and Importing CAD Files
⮚ Linking in Revit Models
⮚ Setting Up Levels
⮚ Copying and Monitoring Elements
⮚ Coordinating Linked Models
⮚ Batch Copying Fixtures
⮚ Modifying the View Display
⮚ Duplicating Views
⮚ Adding Callout Views
⮚ Creating Elevations and Sections
⮚ Connecting Components
⮚ Creating Systems
⮚ Adding Plumbing Fixtures and Equipment
⮚ Adding Plumbing Pipes
⮚ Modifying Plumbing Pipes
⮚ Adding Fire Protection Networks
⮚ Creating and Modifying Systems
⮚ Creating Automatic Layouts
⮚ About Electrical Systems
⮚ Placing Electrical Components
⮚ Creating Electrical Circuits
⮚ Setting up Panel Schedules
⮚ Adding Cable Trays and Conduit
⮚ Testing Electrical Layouts
⮚ Setting Up Sheets
⮚ Placing and Modifying Views on Sheets
⮚ Printing Sheets
⮚ Working with Dimensions
⮚ Working with Text
⮚ Adding Detail Lines and Symbols
⮚ Creating Legends
⮚ Adding Tags
⮚ Working with Schedules
⮚ Setting Up Detail Views
⮚ Adding Detail Components
⮚ Annotating Details
⮚ Introduction to Electrical
⮚ Electrical Basics
⮚ Electricity-Generation, Transmission & Distribution
⮚ Electrical Equipment’s-Transformer, Motor, Generator, UPS etc.
⮚ Switches-one way, 2 way, 3 way, etc
⮚ Measuring Instruments
⮚ Sockets or Receptacle
⮚ Introduction
⮚ Types of Light Fixtures
⮚ LUX or Foot Candle measurement
⮚ LUX Level as per Project
⮚ Light Fixtures calculation as per Standards
⮚ Standard method of lighting placement in project
⮚ Light Fixture Selection Software’s – DIALUX
⮚ Light Fixtures load calculation
⮚ Fan load calculation
⮚ HVAC load calculation
⮚ Plumbing & Fire Fighting load calculation.
⮚ Cables- armored & un armored cables
⮚ Cable Insulation
⮚ Cable type & construction features
⮚ Cable selection
⮚ Cable Routing
⮚ Current rating of cables
⮚ Cable size calculation for motors
⮚ Voltage drop Calculation of Cables
⮚ Application of cable gland & types
⮚ Cable schedule Preparation
⮚ Cable resistance & impedance values
⮚ Cable Lug & its Applications
⮚ Calculation of short circuit withstand capacity of cables
⮚ Installation of cables
⮚ Conduits – types & application
⮚ Conduit selection
⮚ Installation method of conduits
⮚ Cable trays-types, installation procedure, different sizes of cable trays
⮚ Fittings & Accessories of Cable tray
⮚ Cable tray sizing calculation
⮚ Cable tray Routing
⮚ Transformer & its Application
⮚ ypes of Transformers
⮚ Installation standards of Transformer
⮚ Generator & its Application
⮚ Types of Generators
⮚ Generator sizing calculation
⮚ Wiring connections of Generator
⮚ UPS & its application
⮚ Types of UPS
⮚ UPS designing for emergency loads
⮚ Wiring connections of UPS
⮚ Battery Sizing calculation
⮚ Capacitor bank function
⮚ DIALUX
⮚ Plumbing Introduction
⮚ Plumbing – Codes & Standards
⮚ Fundamentals of Plumbing System
⮚ Water Supply System
⮚ Sanitary Drainage System
⮚ Storm Drainage System
⮚ Irrigation System
⮚ Fixture Load as per Codes & Standard
⮚ Hot &Cold Water load
⮚ Water Supply Fixture Unit- WSFU
⮚ Fixture Water Requirement- GPM
⮚ Hot & Cold Water Pipe Size
⮚ Water Distribution – Pipe Routing
⮚ Pipe Joining methods
⮚ Water Supply Demand Calculation
⮚ Storage Tank Types
⮚ Fundamental of Water Supply System
⮚ Sources of Water
⮚ Potable Water Standard
⮚ Water Storage & Consumption
⮚ Domestic Hot and Cold Water Supply
⮚ Water Supply – Commercial & Industrial
⮚ Water Supply Fixtures
⮚ Supply Piping System
⮚ Materials for Piping & Fitting
⮚ Water Supply Controlling Equipment
⮚ Introduction to Water Supply System
⮚ Selection of Booster Pump
⮚ Plumbing Fixtures
⮚ Booster Pumps
⮚ Submersible Pumps
⮚ Boiler and Gaesser
⮚ Water Storage Tanks
⮚ Jacuzzi
⮚ Grease Interceptor
⮚ Plumbing software skills
⮚ Pump calculation
⮚ Pipe size calculation
⮚ Drain Calculation
⮚ Pump calculation
⮚ Pipe size calculation
⮚ Drain Calculation