
Projects require effective management of
various aspects to ensure high-quality outcomes.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology
has emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing
construction quality management. This proposal
outlines the implementation of BIM technology
to streamline quality management processes in
construction projects.

Develop a comprehensive plan outlining the adoption and integration of BIM technology into the construction quality management process. This plan will consider the project requirements, available resources, and the desired
outcomes.

Conduct training programs to familiarize all relevant project stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and subcontractors, with BIM technology and its implementation in quality management processes.

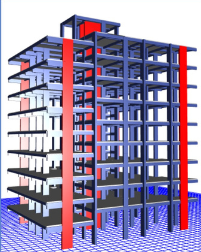
Develop a 3D BIM model that
accurately represents the project’s
design and construction aspects.
This model will serve as a central
repository for project information
and facilitate coordination among
different disciplines.

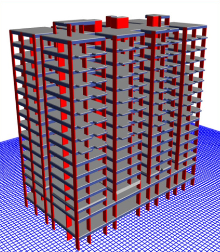
Utilize the BIM model to conduct
thorough design and constructability
reviews. Identify and address any
clashes, conflicts, or inconsistencies in
the design early on, reducing rework
and minimizing errors during
construction
Resolution
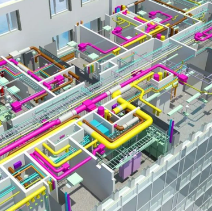
Leverage the clash detection
capabilities of BIM software to identify clashes between different building systems, such as structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing. Resolve clashes collaboratively to ensure seamless coordination and minimize conflicts during construction.

Utilize BIM to monitor construction activities in real-time, capturing
progress, and comparing it with the project schedule. Identify potential delays or issues early on, enabling prompt corrective actions to maintain construction quality and adherence to project timelines.

Implement a centralized BIM platform to facilitate communication and information sharing among project stakeholders. This platform will serve as a common data environment, ensuring that all parties have access to the most up-to-date project information.

Utilize BIM to generate accurate and detailed construction
documentation, including shop drawings, as-built models, and operation and maintenance manuals. This will enhance the quality of project deliverables and improve facility management post-construction.



Enhanced communication and information sharing,
minimizing errors and misunderstandings.


1. PRE-CONSTRUCTION PHASE

By following this comprehensive construction quality
roadmap, project stakeholders can proactively manage
quality throughout the construction process, leading to
successful project outcomes and satisfied clients.








Improve efficiency, provide a better Customer experience with modern Technolo services available
info@e-construct.org
Econstruct Design and Build Pvt Ltd, Venkatadri Heights, 1st & 2nd Floor Parapanna Agrahara Main Road, Opposite Sai Poorna Premier Apartment, Bangalore - 560068
© 2024. All Rights Reserved. ECONSTRUCT DESIGN & BUILD Pvt Ltd.








Improve efficiency, provide a better Customer experience with modern Technolo services available
info@e-construct.org
Econstruct Design and Build Pvt Ltd Venkatadri Heights, 1st & 2nd Floor Parapanna Agrahara Main Road, Opposite Sai Poorna Premier Apartment, Bangalore - 560068
© 2024. All Rights Reserved. ECONSTRUCT DESIGN & BUILD Pvt Ltd.